


The first step is to figure out your business's net profit percentage. Does your business really do well, or are you wasting money that you could be making?
A lot of business owners only care about making money, thinking that high sales mean good performance. You might be celebrating vanity measures instead of real success. Though, if you don't know what's left over after costs. This is where the net profit percentage really makes a difference.
Why the net profit percentage is important Checks operational capacity and true profitability. Allows you to compare yourself to others in the same field and to competitors to see how you do. Finds places to cut costs or improve processes and prices to make more money. This helps you make important choices, such as when to grow, invest, or change your business plan. Boosts investor confidence and makes it easier to get loans or funds.
Whether you run a small business or are a senior leader, knowing how to calculate net profit percentage for your business can tell you a lot about the financial health of your company.
Net profit percentage, which is also called net profit margin. It shows what portion of sales is left over as profit after all costs are taken into account. These costs include taxes, interest, running costs, and other fixed costs. It's a simple but powerful measure that shows how well your company turns sales into real profit.
If you prefer easy tools, using a margin calculator or average calculator can help with fast, accurate estimates.
The net profit percentage, which is also written as net margin, shows how much profit (or net income) a company makes. If you want to show the net profit margin as a number, you can use a decimal instead of a percentage.
The net profit margin tells you how much of every dollar a company makes is profit. To figure it out, divide a company's net income by its total sales and then multiply the result by 100. We'll talk about the net profit margin formula in more detail later in this piece, using both made-up and real-life examples.
Key Takeaways
This number, which is also known as net profit margin, shows how much profit your company makes for every dollar it brings in. Your financial health and how well you use your money are both based on this.
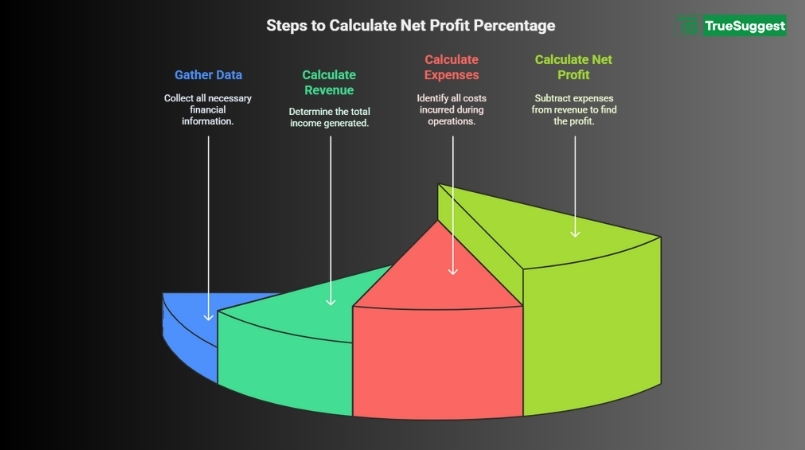
Before you start calculating, collect the necessary numbers from your income statement.
This is the total amount of money made from selling goods or services before any costs are taken out.
Example:
If you sold $100,000 worth of meals, your total revenue = $100,000.
Count up all the money you spend on running your business.
This could mean :
For example,
If all of your costs add up to $75,000, then
Costs added up equal $75,000.
Net profit is the amount that's left over after all costs are taken out of revenue:
Net Profit = Total Sales – Total Costs
To use our example:
$100,000 – $75,000 = $25,000 in net income
Calculating the net profit percentage is a straightforward process. Here’s the formula :
Using the formula of net profit margin, we get –
Net profit margin = Net Profit / Net Sales * 100
Where:
Example
Gross sales 250000
Sales return (-) 5000
--------------------------------
Net sales 245000
Net Profit - $30,000
Net sales - 245000
Net profit margin = 12.24%
Net Profit: This is the actual profit after all expenses have been deducted from total revenue, which includes operating expenses, interest, and taxes. You can also use an online percentage calculator or margin calculator to automate this.
Interpreting Your Net Profit Percentage
Net Profit Percentage, which is also known as net profit margin, is a financial metric that shows what portion of your income is still profit after all costs are taken into account. These costs include taxes, interest, depreciation, and operating costs. How to figure it out:
Net Profit Percentage=(Net Profit / Revenue)×100
Where:
Example
Net Profit Percentage = 7500 / 50000 * 100
= 0.15 = 0.15 * 100 = 15%
Result:
The Net Profit Percentage is 15%, meaning the business earns 15 cents of profit for every dollar of revenue.
What it tells you:
Efficiency: How efficiently your business converts revenue into actual profit.
Profitability: the overall profitability of your business operations.
Cost Control: Whether your costs are in line with your revenue.
If your business makes $1 million in sales and a net profit of $100,000, your net profit rate is 10%. For every dollar you make, you get to keep $0.10.
A "good" net profit margin changes based on the type of business, its stage, and the market it's in.
General guidelines:
Examples by industry:
It is normal for startups and early-stage companies to have low or negative net profit margins because they have to pay a lot of money up front. Use a margin calculator to benchmark and compare across quarters or years. You can even track this using a month calculator or days calculator to evaluate short- or long-term profitability.
Tracking your net profit percentage over time helps identify whether your business is improving or declining in profitability.
Key insights you can gain:
Use tools like a word counter to keep your reports clean and concise and an hours calculator to determine labor-related costs for hourly teams.
Tips for trend analysis:

Increasing sales and lowering costs are both ways to raise your net profit share. Optimizing your prices means making sure they reflect the value you offer and are in line with what the market wants. This could mean raising prices in a way that doesn't turn off customers. Controlling costs is also very important. Look over your bills often and cut back on things that aren't necessary.
Also, renegotiate your supplier contracts and make your operations more efficient. Increasing sales volume through focused marketing, upselling, or entering new markets can also help bring in more money without spending a lot more. Automating and streamlining processes is another important technique that can help cut down on labor costs and boost productivity.
Lastly, focus on high-margin goods or services and think about getting rid of or making better ones that consistently have low margins. If you use these tactics carefully, they can help you increase your net profit percentage over time.
If you want to raise your net profit percentage, you should stay away from common mistakes that can hurt your efforts or lead you astray. Focusing only on cutting costs without thinking about how it will affect quality, customer satisfaction, or staff morale is a big mistake. When you cut costs too much, it can hurt your company and cause you to lose business. People also often make the mistake of raising prices too quickly or for no good reason, which can lose loyal customers and lower total sales.
In addition, companies don't always pay attention to small, ongoing costs that add up and slowly cut into their income. Another mistake is not keeping an eye on your financial information on a daily basis. If you don't, you might miss warning signs or chances to make things better.
Lastly, not comparing your results to industry standards can cause you to have unrealistic hopes or get the wrong idea about the results. By avoiding these common mistakes, you can make sure that your methods for increasing profits work and last.
In conclusion, if you want to build a healthy, long-lasting business, you need to know and keep track of your net profit rate. This key metric gives you a clear picture of how profitable your business is generally and helps you make strategic decisions. You can improve your bottom line and long-term success by correctly reading your margin, setting reasonable goals, looking at long-term trends, and using smart strategies to boost performance. But it's also important to stay away from common mistakes like cutting costs too much or not keeping track of financial data. You can make more money and reach your business goals if you take a balanced, well-informed method.
To calculate net profit percentage in Excel, you can use a simple formula based on your net profit and total revenue (sales).
To find Net Present Value (NPV), you need to use a method that uses a certain discount rate to bring the present value of future cash flows back down to zero.
NPV Formula
Present Value = Cash Flow / (1+i)n
Where:
Example:
Cash Flow (CF) = $1,000
Discount rate (i) = 5% = 0.05
Period (n) = 3 years
Result:
The present value of receiving $1,000 in 3 years at a 5% discount rate is approximately $863.84.